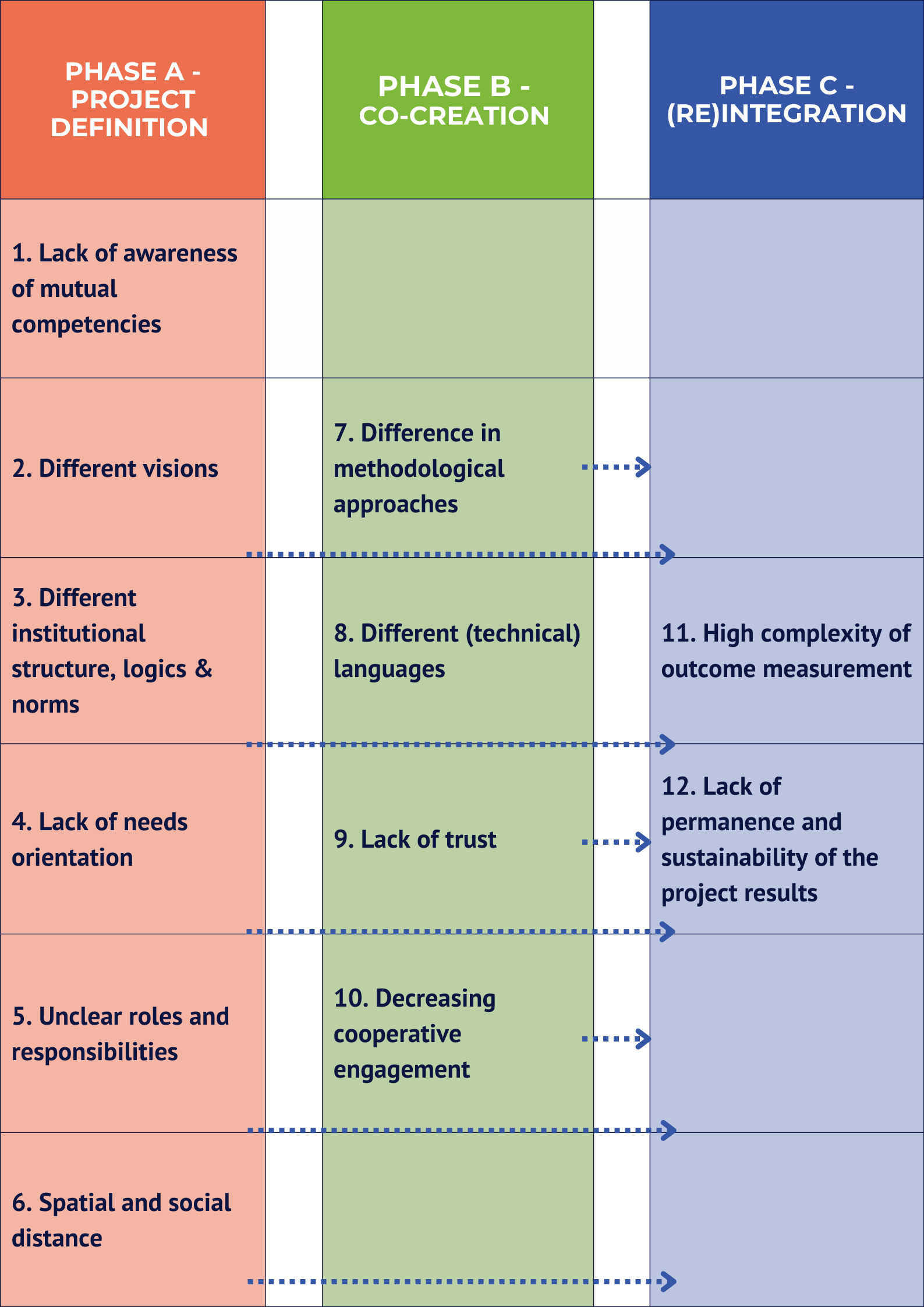
When different disciplines and sectors collaborate, the actors involved repeatedly encounter stumbling blocks that prevent or at least impede successful knowledge and technology transfer. These stumbling blocks are also referred to as transfer barriers.
Transfer barriers were identified on the basis of a systematic literature review. These transfer barriers were compared with the practical experiences from münster.land.leben. The twelve transfer barriers resulting from this process were then assigned to the three project phases.
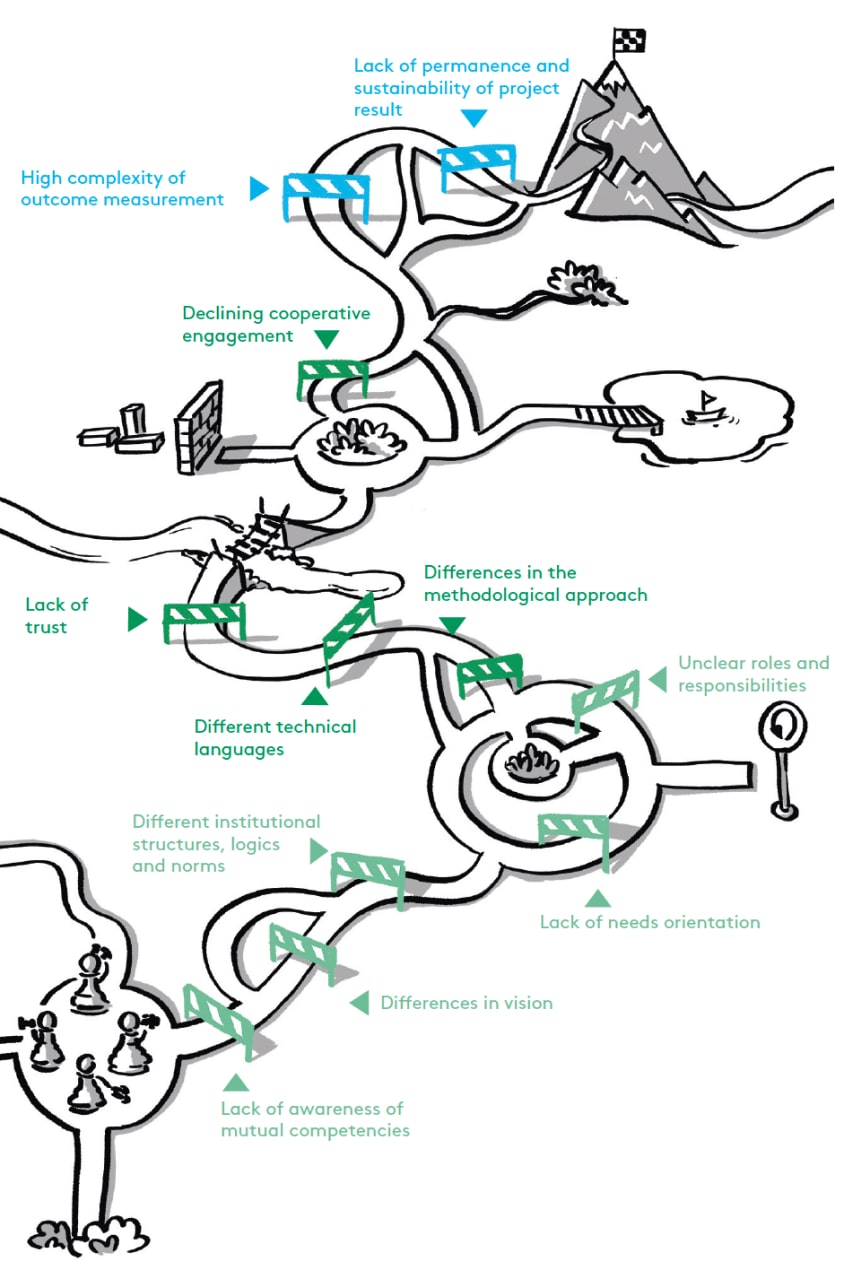
All of the transfer barriers that can occur in the course of a transdisciplinary collaboration are illustrated below. It should be noted here that the course of the project does not always have to be linear, but that the phases with the corresponding transfer obstacles can occur iteratively. In addition, transfer obstacles may not occur at all or may occur in other phases than those assigned in this toolbox, or they may recur in later project phases. The last transfer barrier "spatial and social distance" describes a cross-process transfer barrier that can be applied to all other barriers and their tools. A more detailed description of the transfer obstacles can be found in the whitepaper "gemeinsam.zukunft.gestalten: Knowing and avoiding the main stumbling blocks in transdisciplinary collaborations" (Kurzhals et al. 2021).
The tools and methods contained in the toolbox were each selected to help to overcome a specific transfer barrier. To overcome or address the identified transfer barriers, transfer tools or methods were collected, modified or further developed from the fields of agile management methods such as Scrum, Lean Start-up, Design Thinking, innovation management, creativity management, and empirical social research, among others.
The transfer barriers are the result of a systematic literature research as well as the practical experiences from a regional project in Germany. They shall first raise the awareness for these barriers and thus create the necessary prerequisite to enable the addressing and overcoming of the transfer barriers in a second step with the long-term goal to contribute to the successful implementation of transdisciplinary cooperation projects. Read more in the white paper available for download here: