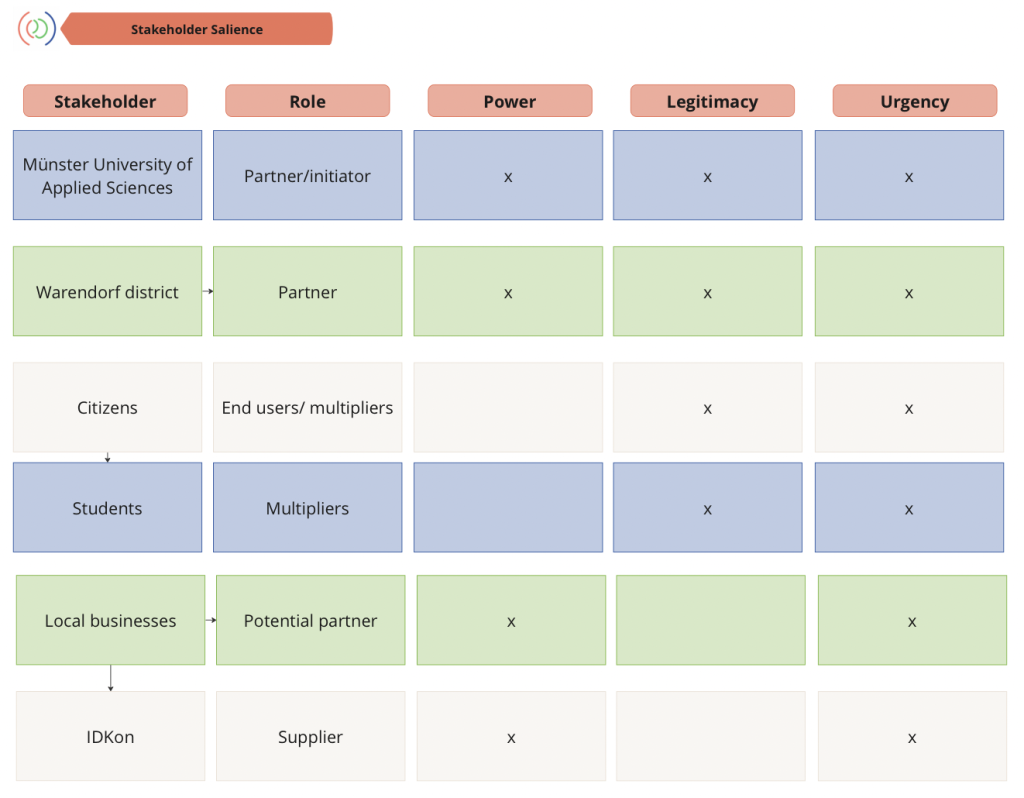
The Stakeholder Salience Model is a strategy tool for segmenting stakeholders. By ranking and evaluating all stakeholders based on three attributes: Power, Legitimacy, and Urgency, an overview and prioritization of all stakeholders who have a claim or interest in the problem and a potential solution is created.