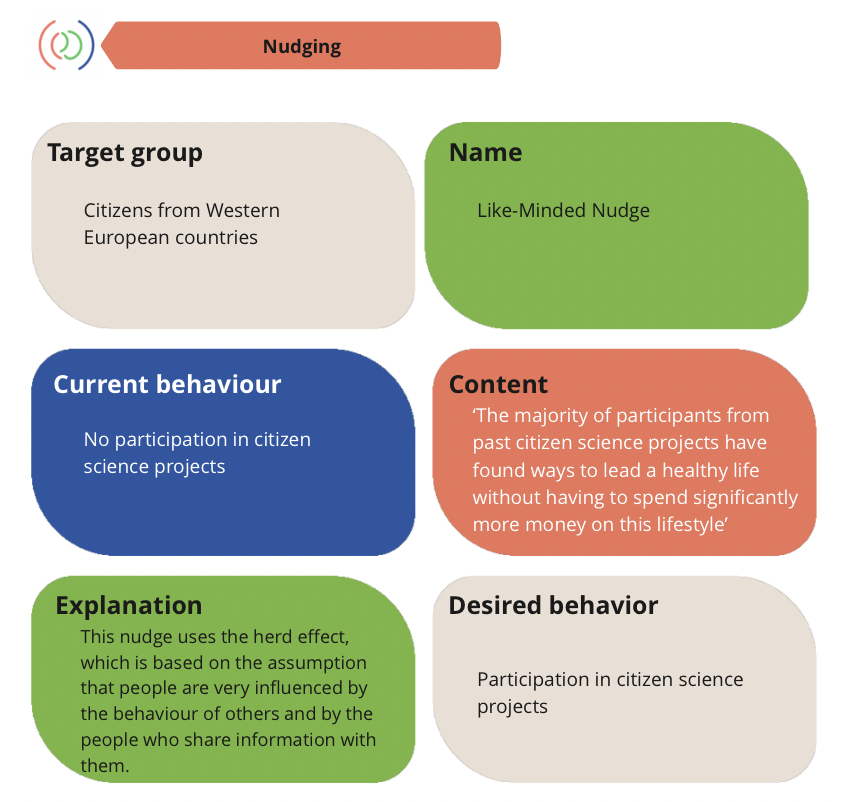
The CoCreAid Kit 4.0 focuses on overcoming barriers to cooperation arising when HEIs and NGOs co-create digitally. By offering a digital platform with various digital tools and methods, the aim is to increase social impact in participating European countries and beyond.